The Science of Cannabis
Understanding Cannabinoids & Terpenes
Cannabis is far more than a single compound or experience. Behind every cannabis plant is a complex chemical profile made up of cannabinoids, terpenes, and other natural compounds that work together to shape how the plant behaves and how it is commonly perceived. Understanding these components helps demystify cannabis and provides a clearer picture of why different strains can feel so distinct.
What Are Cannabinoids?
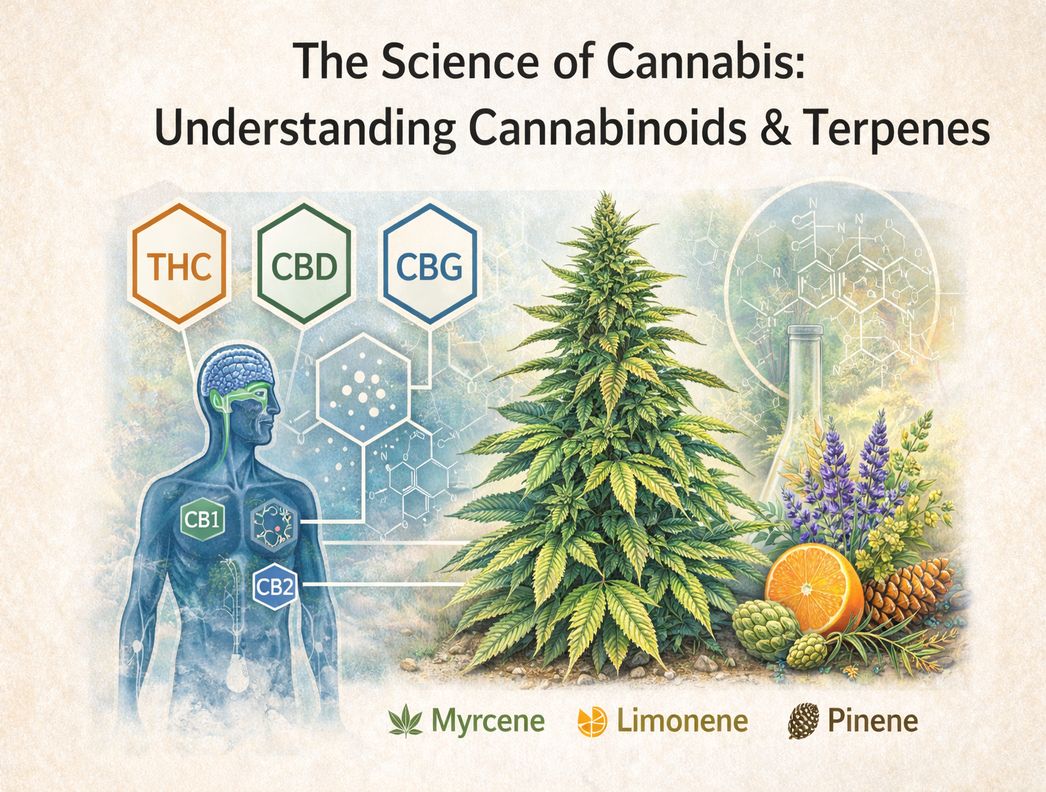
Cannabinoids are naturally occurring compounds found in cannabis plants. To date, scientists have identified more than 100 cannabinoids, each with unique properties and structures. These compounds interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS) - a network of receptors involved in maintaining balance within the body.
The ECS exists naturally in humans and animals, regardless of cannabis use. Cannabinoids from the cannabis plant interact with this system in different ways, which helps explain why strains can produce varied effects.
THC: Tetrahydrocannabinol
THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) is the most well-known cannabinoid. It is primarily responsible for the psychoactive effects commonly associated with cannabis. THC interacts mainly with CB1 receptors, which are found largely in the brain and central nervous system. Because of this interaction, THC-rich strains are often associated with noticeable changes in perception, mood, and sensory awareness. In modern cannabis genetics, THC levels can vary widely depending on strain lineage, cultivation methods, and breeding goals.
CBD: Cannabidiol
CBD (cannabidiol) is another major cannabinoid, but unlike THC, it is non-intoxicating. CBD interacts differently with the endocannabinoid system and does not produce the same psychoactive response.
CBD has become widely recognized for its versatility and presence in both cannabis and hemp varieties. Many modern strains are bred to emphasize specific THC-to-CBD ratios, offering a broad range of cannabinoid profiles for different preferences.
CBG: Cannabigerol
CBG (cannabigerol) is often referred to as a “minor cannabinoid,” but it plays a major role in cannabis chemistry. CBG is considered a precursor cannabinoid, meaning other cannabinoids such as THC and CBD develop from it as the plant matures.
Because CBG typically exists in smaller quantities in mature plants, strains high in CBG are the result of careful breeding and harvesting strategies. Interest in CBG has increased as research continues to explore the full complexity of cannabis compounds.
What Are Terpenes?
Terpenes are aromatic compounds found not only in cannabis but in many plants, fruits, and herbs. They are responsible for the distinctive scents and flavors associated with different cannabis strains, ranging from citrus and pine to earthy or floral notes.
Common cannabis terpenes include:
-
Myrcene – often associated with earthy or musky aromas
-
Limonene – citrus-forward and bright
-
Pinene – pine-like and fresh
-
Caryophyllene – spicy and peppery
Terpenes play an important role in how strains are experienced and are a major factor in strain selection for many consumers.
How Cannabinoids and Terpenes Work Together
Cannabinoids and terpenes do not exist in isolation. They work together within the plant’s chemical profile, contributing to what is often referred to as the “entourage effect.” This concept suggests that the combined presence of cannabinoids and terpenes creates a more nuanced and distinctive experience than any single compound alone. This is why two strains with similar THC levels can feel noticeably different depending on their terpene composition and secondary cannabinoids.
A More Informed Way to Understand Cannabis
As cannabis science advances, the focus is shifting away from simple labels and toward deeper chemical understanding. Cannabinoids and terpenes offer valuable insight into why cannabis strains vary so widely and why modern genetics continue to evolve. Learning about these compounds empowers consumers to make informed choices and highlights the sophistication behind cannabis cultivation and breeding.
